Think
Explore
Attackers use many different methods to obtain personal information so as to steal a victim’s identity. Two popular methods are ‘pharming’ and ‘phishing’. Both methods trick the user into believing the attacker is someone – or something – they’re not. Falling victim to either form attack could cause an individual to lose control of their identity.
Phishing is when the hacker poses as a trustworthy source and asks the victim to give out personal information. Often phishing scams appear to be from legitimate companies.
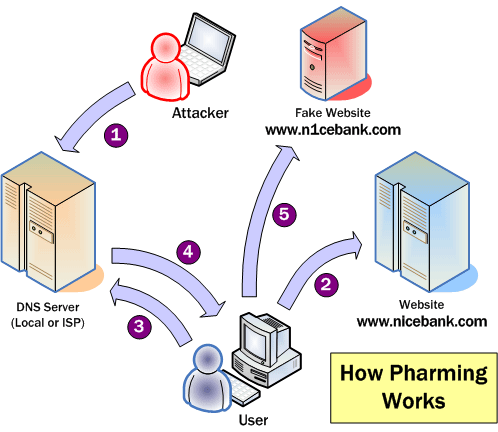
Pharming is a method of identity fraud that takes over a legitimate website or server in order to scam innocent people out of their money. A hacker changes the settings of a server so that when you enter the address of a legitimate website, it redirects you to a fake or a copy of the original site hosted somewhere else. Any data entered on this fake site is then stored on the server of this hacker. The diagram below details how a typical pharming set-up might work. Click on the image to see a larger version, then use your browser’s back button to return to this page.
Image from palisade.plynt.com
![]()
- There are many ways people can try to steal your identity online and offline. So make sure you look after your private data very carefully.
- Pharming is mostly targeted at companies’ websites and not individual users. While legitimate companies try to prevent this by installing defensive software and monitoring their web traffic, there are some things you can do to help protect yourself against pharming.
- Always check that the website has security certificates and that the web address starts with https://
- Read our sections on safety: Wi-fi hotspot security .
- It is still wise to check your bank and credit card statements regularly and report any suspicious charges.
- Online, you might receive a phishing email. Here’s what you need to know:
- Phishing means trying to trick unsuspecting people into giving out personal information such as bank account numbers, passwords, Social Insurance Numbers etc.
- This is usually done through emails that appear to be from legitimate companies, such as banks.
- Never click on any link or submit any information on a website you’ve been sent by email. These links lead to websites that look legitimate but are run by scammers who collect your data to commit fraud.
Links
- Canadian Anti-Fraud Centre
- Mobile pharming – same attacks – different seeds | CSO (2016)
- What is Pharming and how can you prevent this Online Fraud? | The Windows Club (2017)
- What Is Pharming and How Can It Be Prevented? | MakeTechEasier (2017)
- What’s Pharming and How Can You Avoid It? | TechNadu (2018)
- What is Pharming & How to Prevent It? | Kaspersky
- Phishing | Canadian Anti-Fraud Centre
Discuss
The Digital Tattoo Project encourages critical discussion on topics surrounding digital citizenship and online identity. There are no correct answers and every person will view these topics from a different perspective. Be sure to complete the previous sections before answering the questions.
- Have you ever experienced a phishing or pharming attack? What did you do?
- What steps can you take to minimize your risk of falling victim to phishing or pharming?