Blockchain
Blockchain Block Chain Technology Digital Finance – by Tumisu (2017), from Pixabay, used under CC 1.0
Do you ever read an article about Blockchain and wonder what it’s trying to say? I do. With the all hype about Blockchain in news articles/internet headlines, maybe it’s time for Digital Tattoo to look at Blockchain. To simplify things for readers I will do an in-depth investigation, provide research on Blockchain and create graphics to help explain it.
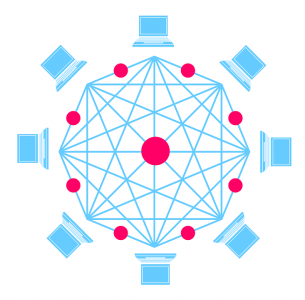
To begin, let’s first look at how Blockchain got its name. Simply put, Blockchain is a system run by people. These people are entrusted with records from other people – otherwise known as data structures – that are submitted through computers. These records grow in lists which are “known as ‘blocks’ in chronological chain.” [1] These blocks are based on a trust system of the people using them.
Think of them as a secure block that cannot be tampered with or manipulated. This is how Stuart Haber and W. Scott Stornetta described these blocks as in 1992. Additionally, “blocks hold batches of valid transactions that are hashed and encoded into a Merkle tree.” [2] What is a Merkle tree? It is described as:
“…..a tree in which every leaf node is labelled with the hash of a data block and every non-leaf node is labelled with the cryptographic hash of the labels of its child nodes. Hash trees allow efficient and secure verification of the contents of large data structures. Hash trees are a generalization of has lists and hash chains.” [3]
These systems are decentralized, but unlike a bank chain storing your information, they are distributed through a system of people using their own personal computers. This means anyone can use Blockchain to help run and keep the system safe and secure. It is more difficult to be corrupted or take down a network, which is what makes distribution so important. This is unlike centralized systems, which are prone to this. With a decentralized network, it is not as easy for hackers to pinpoint. [4]
How does Blockchain make sure that they cannot be corrupted or manipulated? They use Cryptography. Cryptography is a type of math or coding which eliminate records being counterfeited or manipulated by others. Although Blockchain uses coding to create it, it is still easy to read by the end user. [5]
To summarize, Blockchain allows users to bypass the mediator stage while making transactions. [6] Thus, you can keep your transactions safe with the use of a unique key that seals the pages of your transactions by the entrusted people in Blockchain. [7]
As with any new emerging technology, it is good to check facts before investing in it. To learn more about Blockchain, here are some resources to help you decide if this new technology is right for you:
Forbes: “What Exactly is Blockchain, And Should You Adopt Its Technology?”.
Blockgeeks: “What is Blockchain Technology? A Step-by-Step Guide”.
Hacker Noon: “WTF is The Blockchain?”.
Hackner Noon: “Learn Blockchains by Building One”.
Medium, FreeCodeCamp: “How does blockchain really work? I built an app to show you”.
Medium: “Self Sovereign Identity- a guide to privacy for your digital identity with Blockchain”.
Edited by: Defne Inceoglu


You made some good points there. I did a search on the issue and found most people will consent with your site.